The wheel-driven land speed record differs from the absolute land speed record in requiring that the vehicle be wheel-driven; thus, jet engine and rocket propelled vehicles are ineligible.
Until
1963, the absolute land speed record holder was always a wheel-driven
car. The first jet-car to exceed the absolute record was Craig Breedlove's Spirit of America. Since then, no wheel-driven car has held the absolute record.
There is no "wheel-driven" category as such.[1]
The Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile validates records in a
variety of classes, of which the "wheel-driven" classes are in Category
A (Special cars) and Category B (Production cars). The accepted record
is fastest average speed recorded over one mile or one kilometer with a
flying start, averaged over two runs in opposite directions within one
hour of each other. The most recent Wheel-driven" record holders have
been from a variety of different classes within Category A.[2]
Since 1963, holders of the wheel-driven land speed record have been:
| Date |
Location |
Driver |
Vehicle |
Power |
Speed over
1 km |
Speed over
1 mile |
Notes |
| mph |
km/h |
mph |
km/h |
| September 16, 1947 |
Bonneville Salt Flats, USA |
 John Cobb John Cobb |
Railton Mobil Special |
IC |
393.82 |
633.79 |
394.19 |
634.39 |
First 400 mph (640 km/h) pass |
| July 17, 1964 |
Lake Eyre, Australia |
 Donald Campbell Donald Campbell |
Bluebird CN7 |
Turboshaft |
— |
403.10 |
644.96 |
FIA's official absolute record-holder till a change in the rules in December 1964 made jetcars eligible.[3] |
| November 13, 1965 |
Bonneville Salt Flats, USA |
 Bob Summers Bob Summers |
Goldenrod |
IC |
— |
409.277 |
658.526 |
Still the non-supercharged piston-engine record[2]Group II, Class 11:[4] 2 or 4 stroke engine without supercharger, cylinder capacity > 8000 cm³[5] |
| August 21, 1991 |
Bonneville Salt Flats, USA |
 Elwin "Al" Teague Elwin "Al" Teague |
Spirit of '76 (Torque Speed-o-Mative Streamliner) |
supercharged hemi |
425.050 |
684.052 |
409.978 |
659.796 |
Still the piston-engined record[2] Group I, Class 11:[4] 2 or 4 stroke engine with supercharger, cylinder capacity > 8000 cm³[5] |
| October 18, 2001 |
Bonneville Salt Flats, USA |
 Don Vesco Don Vesco |
Vesco Turbinator |
Turboshaft |
458.196 |
737.395 |
458.444 |
737.794 |
[2]Group IX, Class 3:[4] Turbine engine, unloaded weight > 1000 kg[5] |
| September 26, 2008 | Bonneville Salt Flats, USA |  Tom Burkland Tom Burkland | Burkland 411 Streamliner | IC supercharged hemi | - | - | 415.896 | 669.319 | Piston-engined record[2] Group I, Class 11:[4] 2 or 4 stroke engine with supercharger, cylinder capacity > 8000 cm3[5] | | September 21, 2010 | Bonneville Salt Flats, USA |  Charles E. Nearburg Charles E. Nearburg | Spirit of Rett streamliner | IC General Motors V8 | 414.477 | 667.037 | 414.316 | 666.776 | Non-supercharged piston-engine record[2] Group II, Class 11:[4] | | September 17, 2012 | Bonneville Salt Flats, USA |  George Poteet George Poteet | Speed Demon Streamliner | IC Hellfire | 439.562 | 707.408 | 439.024 | 706.540 | Piston-engined record[2] 2 or 4 stroke engine with supercharger, Category A, Group 1, Class 10 |
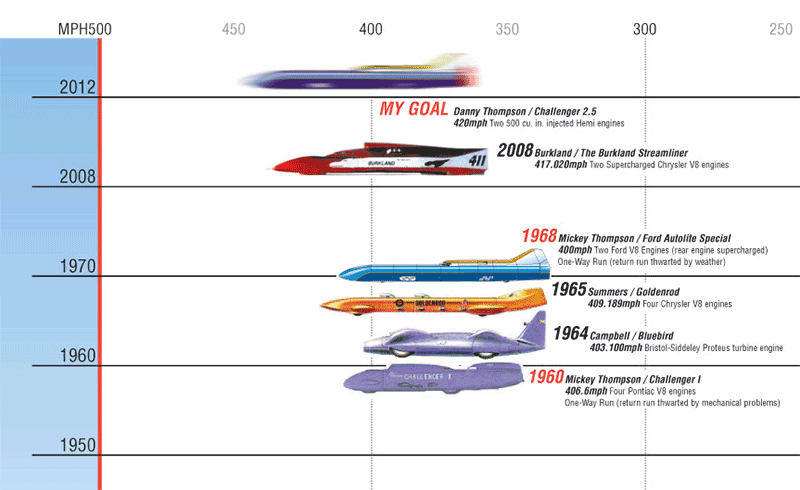

Graphic Supplied by Danny Thompson
See also
References
- ^ Fadini, Ugo (20 August 2002). "Who holds the "wheel-driven" LSR?". http://www.ugofadini.com/lsrwdold.html. Retrieved on 2008-11-09.
- ^ a b c d Fadini, Ugo (17 August 2002). "Don Vesco becomes undisputed holder of the "wheel-driven" LSR". http://www.ugofadini.com/lsrwdnew.html. Retrieved on 2008-11-09.
- ^ "from our motoring correspondent" (Saturday, Dec 12, 1964). "Land Speed Record Agreement". The Times (Issue 56193): p. 7, col E.
- ^ a b c d e "List of Records Category A" (in French) (PDF). FIA. 2008-06-05. http://argent.fia.com/web/fia-public.nsf/AB19CCBEAE22D41BC125745F00375686/$FILE/Liste%20Records%20Cat%20A.pdf. Retrieved on 2008-11-06.
- ^ a b c d "Appendix B: Category A". Records. FIA. http://www.fia.com/en-GB/sport/records/appendixb/Pages/CategoryA.aspx. Retrieved on 2008-11-09.
|